Ball Corporation (NYSE:BLL) Has A ROE Of 16%

One of the best investments we can make is in our own knowledge and skill set. With that in mind, this article will work through how we can use Return On Equity (ROE) to better understand a business. To keep the lesson grounded in practicality, we'll use ROE to better understand Ball Corporation (NYSE:BLL).
Return on equity or ROE is an important factor to be considered by a shareholder because it tells them how effectively their capital is being reinvested. Put another way, it reveals the company's success at turning shareholder investments into profits.
View our latest analysis for Ball
How Is ROE Calculated?
Return on equity can be calculated by using the formula:
Return on Equity = Net Profit (from continuing operations) ÷ Shareholders' Equity
So, based on the above formula, the ROE for Ball is:
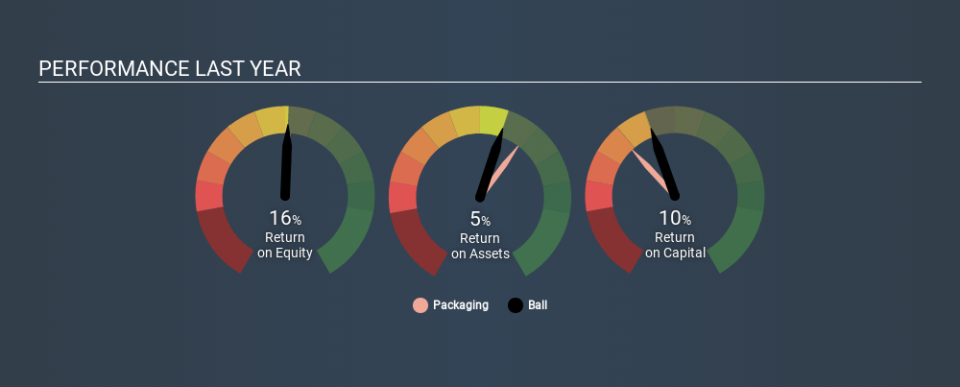
16% = US$442m ÷ US$2.7b (Based on the trailing twelve months to March 2020).
The 'return' is the income the business earned over the last year. That means that for every $1 worth of shareholders' equity, the company generated $0.16 in profit.
Does Ball Have A Good ROE?
Arguably the easiest way to assess company's ROE is to compare it with the average in its industry. The limitation of this approach is that some companies are quite different from others, even within the same industry classification. If you look at the image below, you can see Ball has a similar ROE to the average in the Packaging industry classification (17%).
So while the ROE is not exceptional, at least its acceptable. Even if the ROE is respectable when compared to the industry, its worth checking if the firm's ROE is being aided by high debt levels. If so, this increases its exposure to financial risk. To know the 2 risks we have identified for Ball visit our risks dashboard for free.
Why You Should Consider Debt When Looking At ROE
Virtually all companies need money to invest in the business, to grow profits. That cash can come from issuing shares, retained earnings, or debt. In the first two cases, the ROE will capture this use of capital to grow. In the latter case, the debt used for growth will improve returns, but won't affect the total equity. That will make the ROE look better than if no debt was used.
Combining Ball's Debt And Its 16% Return On Equity
Ball clearly uses a high amount of debt to boost returns, as it has a debt to equity ratio of 2.96. While its ROE is pretty respectable, the amount of debt the company is carrying currently is not ideal. Debt increases risk and reduces options for the company in the future, so you generally want to see some good returns from using it.
Summary
Return on equity is a useful indicator of the ability of a business to generate profits and return them to shareholders. A company that can achieve a high return on equity without debt could be considered a high quality business. If two companies have the same ROE, then I would generally prefer the one with less debt.
But ROE is just one piece of a bigger puzzle, since high quality businesses often trade on high multiples of earnings. The rate at which profits are likely to grow, relative to the expectations of profit growth reflected in the current price, must be considered, too. So you might want to take a peek at this data-rich interactive graph of forecasts for the company.
But note: Ball may not be the best stock to buy. So take a peek at this free list of interesting companies with high ROE and low debt.
Love or hate this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.

 Yahoo Finance
Yahoo Finance